networktestinggenius.tk
Your networking tutor
Exclusive networking testing notes
Learn Networking & Testing topics

-
Distance vector
-
Routing updates every 30 Seconds
-
Full routing table periodic updates
-
Uses distance as a metric
-
Supports IP and IPX routing
-
Uses UDP port 520
-
AD value is 120
-
Hop count is 16
-
16th Hop is poisonous or infinite
-
RIPv1 is a classful routing protocol, RIPv2 is classless protocol.
-
RIPv1 use broadcast to update the routing table, RIPv2 uses multicasts (224.0.0.9) rather than broadcasts to 255.255.255.255.
-
RIPv1 don’t support VLSM, RIPv2 supports VLSM
-
RIPv1 don’t support manual route summarization, RIPv2 support manual route summarization.
-
RIPv2 supports MD5 authentication for routing updates


Split Horizon
A split horizon is a routing configuration that stops a route from being advertised back in the direction from which it came. Split Horizon mechanism states that if a neighbouring router sends a route to a router, the receiving router will not propagate this route back to the advertising router on the same interface.
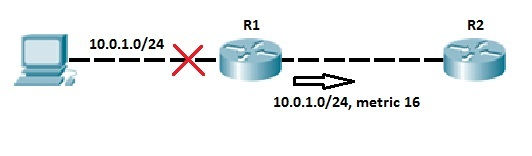
Route Poisoning
Route Poisoning is another method for avoiding routing loops. When a router detects that one of its connected routes has failed, the router will poison the route by assigning an infinite metric to it.
Hold-down Timers
Hold-down timer is another mechanism used to prevent bad routes from being restored and propagated by mistake. When a route is placed in a hold-down state, routers will neither advertise the route nor accept advertisements about it for a specific interval called the hold-down period.
-
Update: this is how often we send routing updates, the default is 30 seconds.
-
Invalid: the number of seconds since we received the last valid update, once this timer expires the route goes into holddown, the default is 180 seconds.
-
Holddown: the number of seconds that we wait before we accept any new updates for the route that is in holddown, the default is 180 seconds,
-
Flush: how many seconds since we received the last valid update until we throw the route away, the default is 240 seconds.
R1
interface Loopback0
ip address 192.169.1.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
router rip
network 192.168.1.0
network 192.169.1.0
R2
interface Loopback0
ip address 192.169.2.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
router rip
network 192.168.1.0
network 192.168.2.0
network 192.169.1.0
network 192.169.2.0
show ip protocols
show ip route
ping
debug ip rip
passive-interface

Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Key notes
Timers
How Loop occurs
RIP V1 vs V2
Basic Configs
External links
Loop avoidance

1.When network 5 fails router E tails Router C to stop routing to network 5 through Router E
2.But A,B,D Routers don't know about network 5,so they keep sending information
3.C Router forward to B network 5 is fail so don't send update to C Router threw network 5
4.Still A,D Routers are not updated
5.Problem occurs when Router A sends its update after 30 seconds to reach network 5 .at this time B,D Routers receives a wonder news network 5 can be reached from Router A
6.So,B,D Routers send that network 5 available
7.Any packet will go for network 5 with Router A to Router B and then back to Router A
Detailed working
When we start this network, Routers are aware only about the directly connected network.
R1
Network port
10.0.0.0/8 Fa0/0
20.0.0.0/8 s0/0/0
R2
Network port
30.0.0.0/8 Fa0/0
20.0.0.0/8 s0/0/0
R1 will listen broadcast from R2. From R2 it will learn one new network 30.0.0.0
R1
Network port
10.0.0.0/8 Fa0/0
20.0.0.0/8 s0/0/0
30.0.0.0/8 Fa0/0
R2 will listen broadcasts from R1 10.0.0.0
R2
Network port
30.0.0.0/8 Fa0/0
20.0.0.0/8 s0/0/0
10.0.0.0/8 Fa0/0
Examine the routing table
C 10.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
C 20.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
R 30.0.0.0/8 [120/1] via 20.0.0.2, 00:00:27, Serial0/0/0

Key notes
-
RIP routing protocol uses local broadcast to share routing information.
-
RIP broadcasts routing updates in every 30 seconds, regardless something in network has changed or not. Once 30 seconds expires, routers running RIP protocol will broadcast their routing information to any devices connected to their interfaces.
-
Before sending routing updates router add a initiating metric to every routes which it has and increments the metric of incoming routes in advertisements so the listing router can learn how far destination network is.
-
While sending broadcasts RIP does not care about who listens these broadcast updates or not.
-
After sending broadcast RIP does not care whether neighbors received these broadcast updates or not.
-
When router receives routing updates, it compares them with the routes which it already has in its routing table.
-
If update has information about a route which is not available in its routing table, router will consider that route as a new route.
-
Router will add all new routes in routing table before updating existing one.
-
If update has better information for any existing route, router will replace old entry with new route.
-
If update has worse information for any existing route, router will ignore it.
-
If update has exactly same information about any existing route, router will reset the timer for that entry in routing table.
The administrative distance of RIP is 170, is that right?
No
Does RIPv1 support Classless routing?
RIPv1 does not support classless routing. RIPv2 support classfull and classless routing both.
Is RIP v2 is link state protocol?
No, it is distance vector protocol
Which protocol does RIP use to transport data?
RIP use UDP
Home many types of RIP messages?
There are two type of RIP messages, these are request and respond.
Ask yourself
-
What is Route Poisoning?
-
What is Split Horizon ?
-
Utilizing RIP, what is the limit when it comes to number of hops?
-
What is the difference between RIP V1 and V2 ?
-
Mulitcast address of RIP v2 ?
-
Administristative distance of RIP ?
-
Can we use RIP in a scenario having more than 15 routers ?
-
What is the difference between RIP and RIPng?